-
Koszyk jest pusty!
MENU
Amputacja (z łac. Amputatio), używana jest także nazwa odjęcie – zabieg operacyjny polegający na usunięciu narządu lub jego części. Nazwa ta jest używana przede wszystkim w odniesieniu do operacji usunięcia kończyny górnej lub dolnej, przebiegającej z przecięciem kości i wytworzeniem kikuta. Amputacje kończyny określa się od wysokości, na której następuje odjęcie i tak np. amputacja udowa, to odjęcie kończyny na wysokości uda z przecięciem kości udowej. Amputacja jest jednym z najstarszych zabiegów chirurgicznych, znanym już w starożytności. W nomenklaturze ortopedycznej wyróżniamy amputacje oraz wyłuszczenie w stawie.
Amputacja – zabieg operacyjny polegającego na usunięciu narządu lub jego części. Przykładem może być amputacja podudzia oraz amputacja Syma.
Wyłuszczenie - odjecie kończyny przebiega poprzez rozdzielenie kości w stawie, a nie jej przecięcie. Przykładem może być wyłuszczenie w stawie nadgarstkowym, wyłuszczenie w stawie kolanowym i amputacja wyłuszczenie w stawie biodrowym.
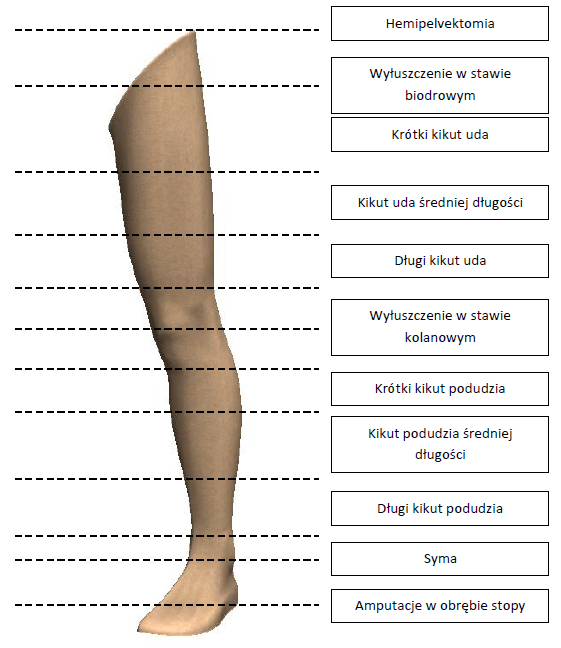
Hemipelvektomia - Amputacja z częściową resekcją miednicy oraz talerza biodrowego. Konieczna najczęściej w przypadku nowotworów. Zaopatrzenie protetyczne może stanowić proteza całej kończyny dolnej z kosztem biodrowym. Podczas chodzenia wymaga dużego wkładu energetycznego.
Wyłuszczenie w stawie biodrowym - Wyłuszczenie z odjęciem kończyny w stawie biodrowym, bez przecięcia kości. Konieczna najczęściej z przyczyn chorobowych – nowotwór, rzadziej traumatologicznych. Zaopatrzenie protetyczne może stanowić proteza całej kończyny dolnej z kosztem biodrowym. Podczas chodzenia wymaga dużego wkładu energetycznego.
Krótki kikut uda – Amputacja przez kość udową z zachowaniem mniej niż 35% jej długości. Konieczna najczęściej w wyniku powikłań urazowych. Zaopatrzenie protetyczne może stanowić proteza udowa. W niektórych przypadkach stosowana dodatkowo do stabilizacji szyna biodrowa lub łuk biodrowy. Podczas chodzenia znacznie obniżona funkcjonalność. W większości przypadków powstaje przykurcz zgięciowy, dochodzi do rotacji i odwiedzenia kikuta na zewnątrz.
Kikut uda średniej długości – Amputacja przez kość udową z zachowaniem 35-60% jej długości. Konieczna najczęściej w wyniku powikłań urazowych. Zaopatrzenie protetyczne może stanowić proteza udowa. Podczas chodzenia kikut średnio wydolnościowy. Powszechnie spotykany, długość stosowana przy planowanej amputacji, pozwala na dowolny dobór komponentów protetycznych i leja protezowego.
Długi kikut uda – Amputacja przez kość udową z zachowaniem powyżej 60% jej długości. Konieczna najczęściej w wyniku powikłań urazowych. Zaopatrzenie protetyczne może stanowić proteza udowa. Podczas chodzenia kikut średnio wydolnościowy. Rzadko spotykany, ze względu na brak mięśni w części dystalnej kikuta. Kikuty zwykle posiadają kształt stożkowy z mocno uwydatnioną na szczycie kością udową.
Wyłuszczenie w stawie kolanowym – Wyłuszczenie z odjęciem kończyny w stawie kolanowym, bez przecięcia kości. Konieczna najczęściej w wyniku powikłań urazowych. Zaopatrzenie protetyczne może stanowić proteza udowa. Podczas chodzenia kikut najbardziej wydolnościowy z amputacji na poziomie uda. Problemy przy doborze protetycznego przegubu kolanowego, ze względu na małą odległość od kikuta do osi obrotu stawu kolanowego.
Krótki kikut podudzia – Amputacja przez kość piszczelową, następuje całkowite usunięcie kości strzałkowej. Zachowane jest mniej niż 25% długości kości piszczelowej. Głównym celem jest zachowanie stawu kolanowego. Konieczna najczęściej w wyniku powikłań urazowych. Zaopatrzenie protetyczne może stanowić proteza podudzia. Podczas chodzenia trudności w sterowaniu protezą. Proteza wyposażona najczęściej w mankiet udowy. W większości przypadków powstaje przykurcz zgięciowy w stawie kolanowym oraz niestabilność boczna stawu kolanowego.
Kikut podudzia średniej długości - Amputacja przez kość strzałkową i piszczelową z zachowaniem 25-45% jej długości. Konieczna najczęściej w wyniku powikłań urazowych. Zaopatrzenie protetyczne może stanowić proteza podudzia. Podczas chodzenia kikut najbardziej wydolnościowy z amputacji na poziomie podudzia. Powszechnie spotykany, długość stosowana przy planowanej amputacji, pozwala na dowolny dobór komponentów protetycznych i leja protezowego.
Długi kikut podudzia – Amputacja przez kość strzałkową i piszczelową z zachowaniem powyżej 45% jej długości. Konieczna najczęściej w wyniku powikłań urazowych. Zaopatrzenie protetyczne może stanowić proteza podudzia. Podczas chodzenia kikut średnio wydolnościowy. Rzadko spotykany, ze względu na niewielką ilość tkanek miękkich w części dystalnej. Pozostają jedynie ścięgna oraz skóra, przez co nawet przy dobrze zachowanym krwioobiegu kikut ma tendencje do oziębiania się. Problemy przy doborze stopy protezowej, ze względu na małą odległość od kikuta do podłoża.
Syma - Amputacja całej stopy z usunięciem powierzchni stawowej kości piszczelowej, obu kostek bocznej i przyśrodkowej, pokrycie kikuta płatem skórno-mięśniowym spod pięty. Konieczna najczęściej z przyczyn chorobowych – cukrzyca, problemy z układem krążenia, rzadziej traumatologicznych. Zaopatrzenie protetyczne może stanowić specjalna stopa protezowa.
Amputacje w obrębie stopy – Dla rejonu stopy wyróżniamy ponad dwanaście różnych poziomów amputacji. W skład tych zabiegów wchodzi amputacja palców stopy, poprzez amputację śródstopia aż do amputacji w rejonie stępu. Konieczna najczęściej z przyczyn chorobowych – cukrzyca, problemy z układem krążenia, rzadziej traumatologicznych. Zaopatrzenie protetyczne może stanowić indywidualnie wykonana silikonowa epiteza lub proteza.